Scabies is a common condition caused by an allergic reaction to tiny mites which burrow under the skin to lay their eggs.
It is important to treat scabies as quickly as possible to prevent it spreading to other people and to prevent the symptoms from getting worse.
The symptoms normally include:
Scabies can be spread from one person to another through longer-lasting skin to skin contact.
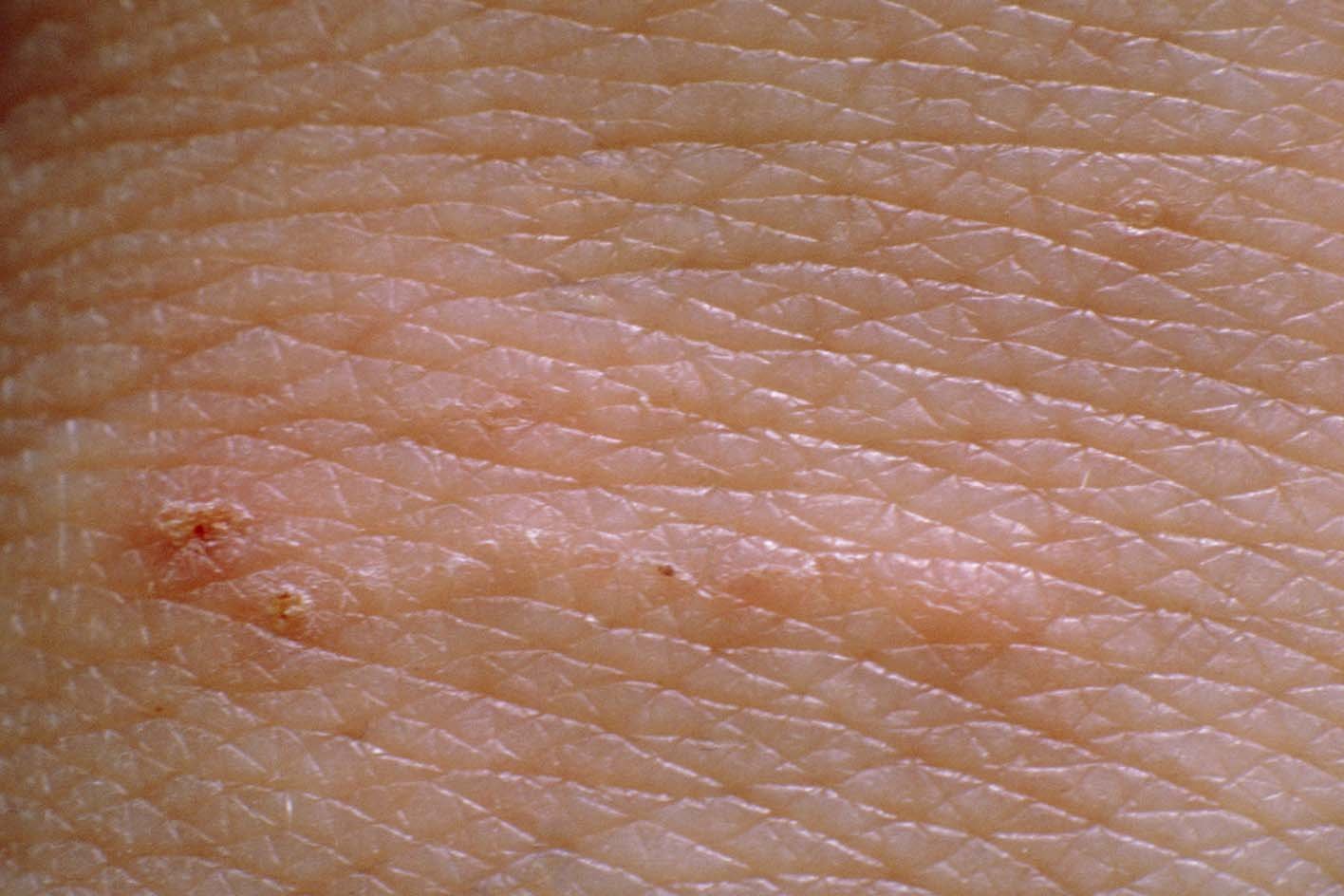
Tiny mites lay eggs in the skin, leaving lines with a dot at one end.
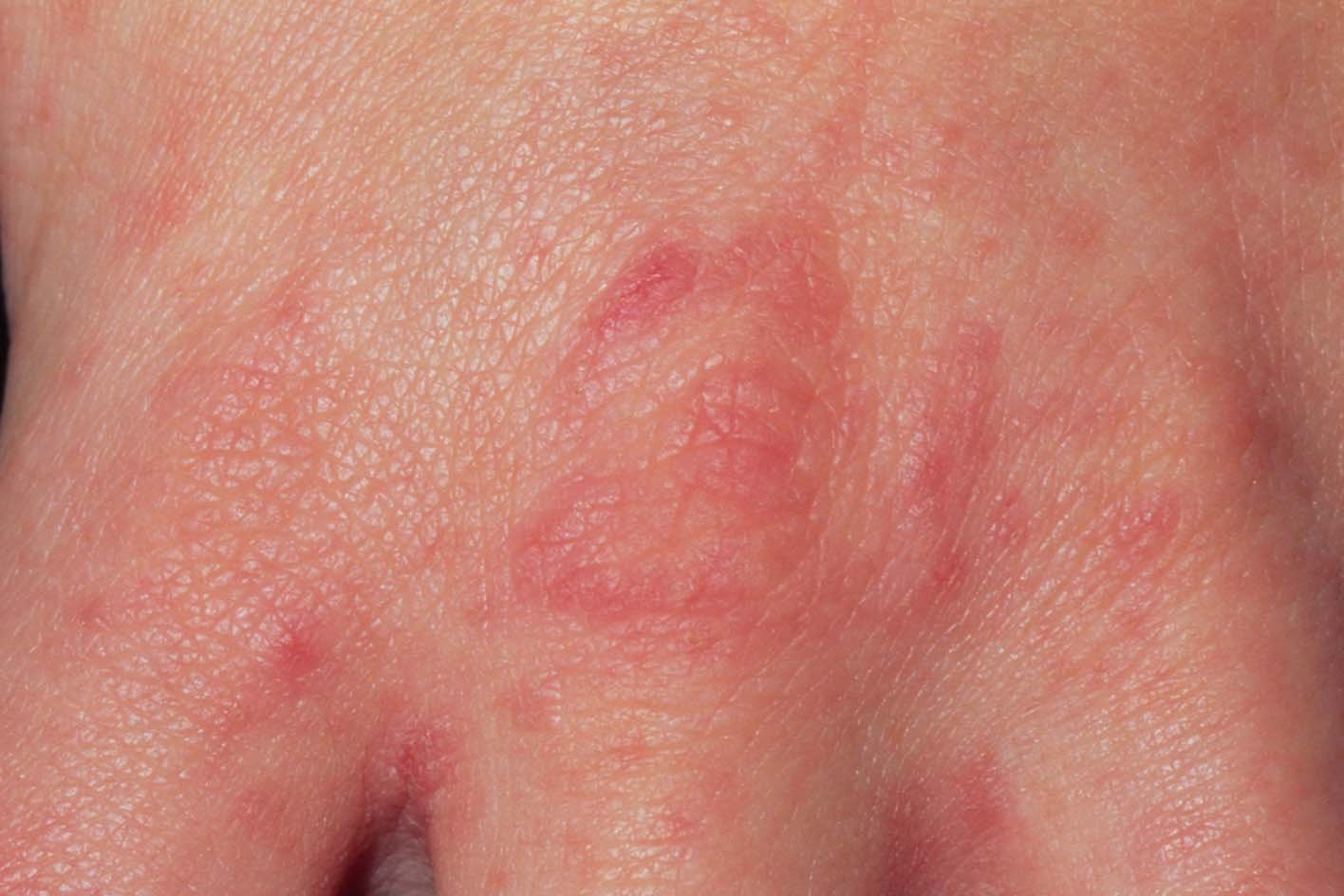
The rash can appear anywhere, but it often starts between the fingers.
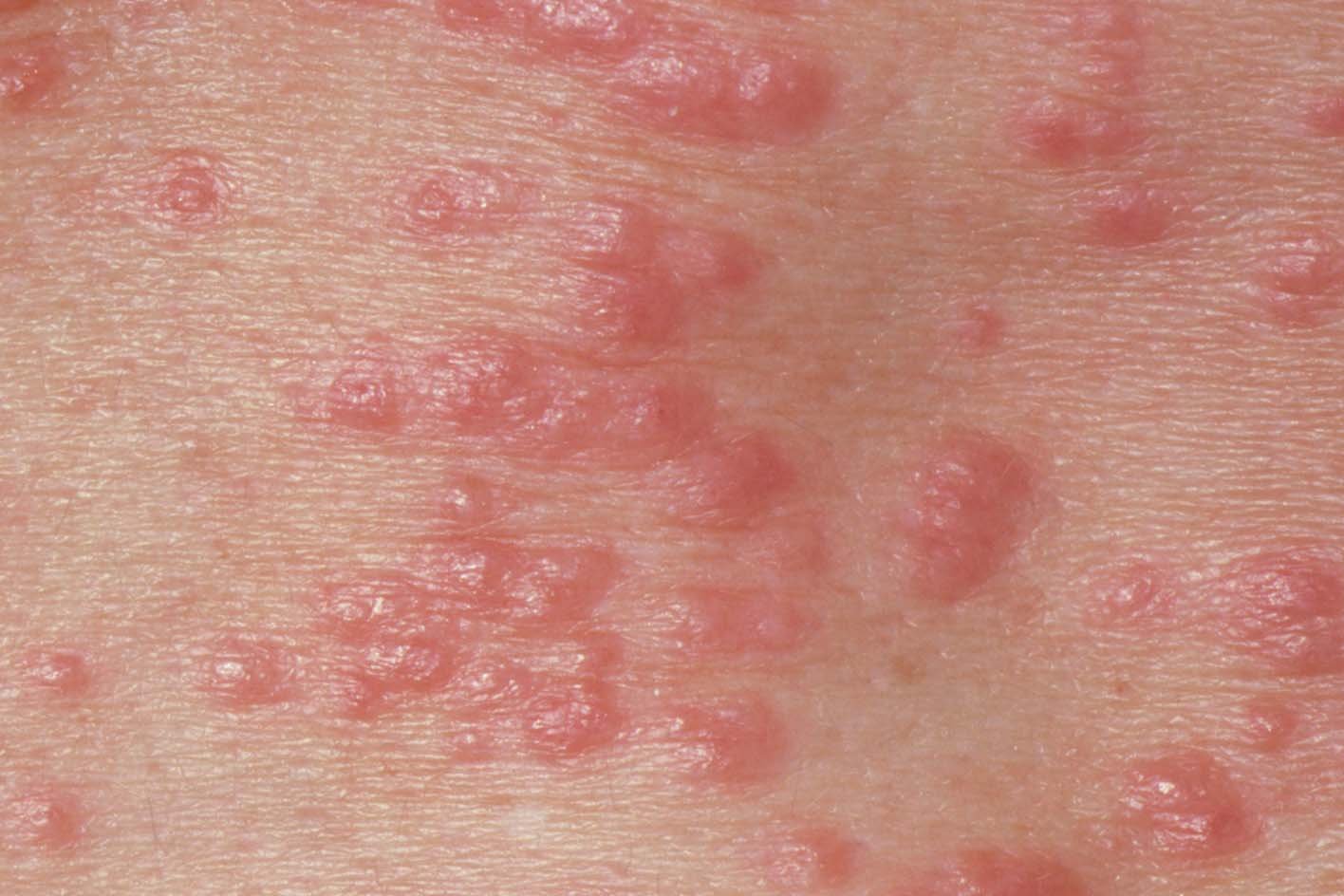
The rash may then spread and turn into tiny spots. This may look red on lighter skin.
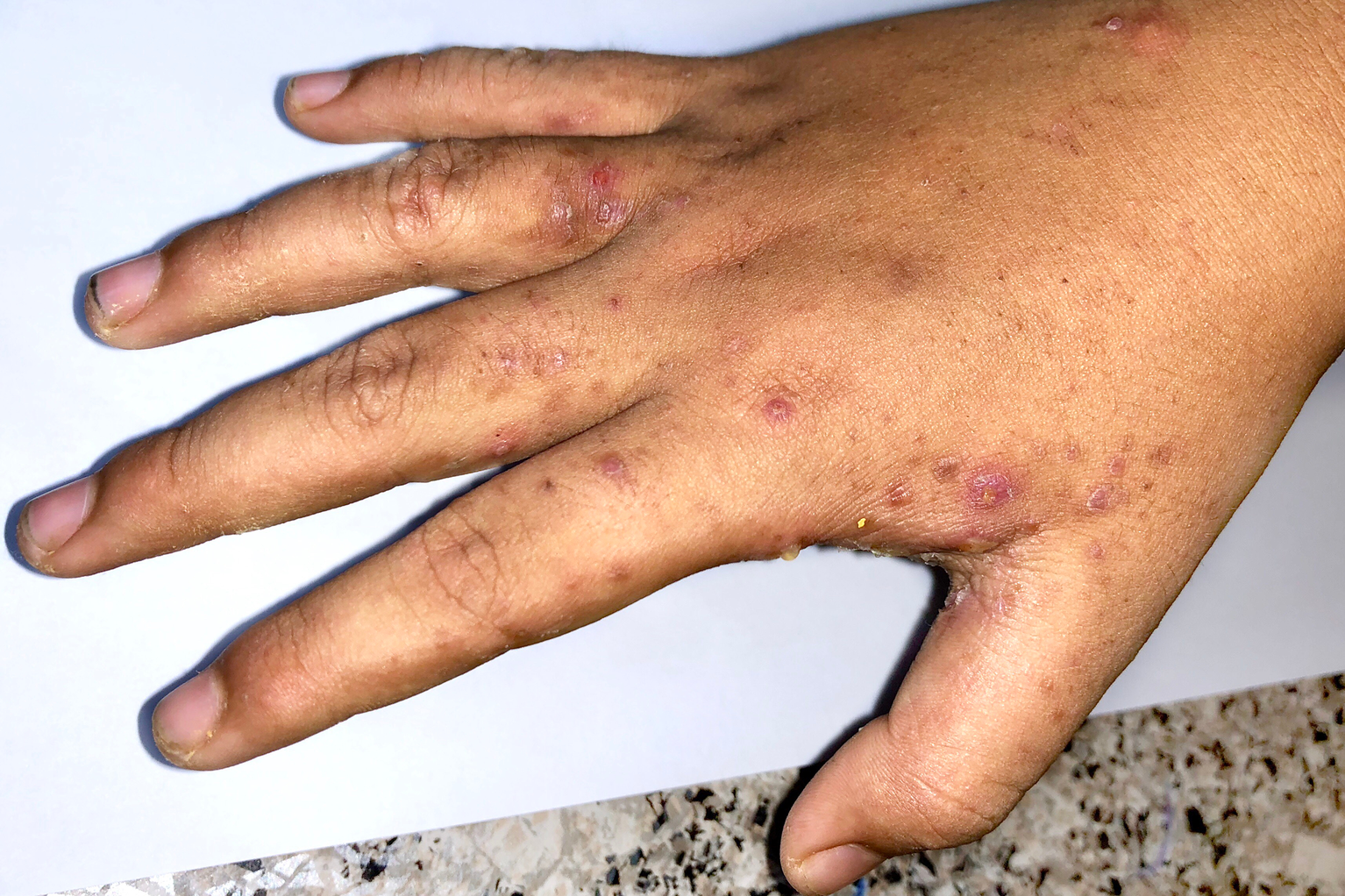
The rash may leave dark spots on the skin. This may look brown or black on darker skin.
Crusted scabies, or Norwegian Scabies, is a rare but more severe form of the condition, where a large number of mites are in the skin. In crusted scabies, the increase in the number of mites causes thick, warty crusts to develop on the skin. Unlike normal scabies, the rash associated with crusted scabies usually doesn't itch. Crusted scabies is more likely to develop in older people and those with a lowered immunity.
Treatment
The usual treatment is either a cream containing permethrin or a lotion containing malathion. These will kill the mites.
A pharmacist can recommend the correct treatment, or it can be prescribed by a GP. You should tell the pharmacist if the treatment is for pregnant or breastfeeding women, or babies under six months old.
How To Stop Scabies Spreading
As well as skin treatments, the following practical advice will help to prevent scabies spreading.
You can contact the Healthy Child Programme by calling Just One Number on 0300 300 0123 or texting Parentline on 07520 631590. Our opening hours are 8am-6pm Monday-Friday (excluding bank holidays) and 9am-1pm on Saturdays.
If you are 11-19 you can text ChatHealth on 07480 635060 for confidential advice from one of our team.
The Lullaby Trust - Baby Check App - This app has simple checks that you can do if your baby is ill and helps you think about whether they need to see a doctor or health professional.
app has simple checks that you can do if your baby is ill and helps you think about whether they need to see a doctor or health professional.
You can speak to other Norfolk parents and carers by clicking our online community forum below.